Theme:
Cell Signaling 2021
Cell Signaling 2021 conference invites all the participants across the globe to attend and share their insights and convey recent development technologies and methodologies in the field of Cell Signaling and Cancer Therapy based on the theme “To support Cancer Therapy Research from bench to clinic” which will be held during November 24-25, 2021 at Webinar. We are pleased to welcome all Biologists, Scientists, Delegates, Speakers, Specialists of Cell Signaling and Cancer Therapy to attend the Conference.
Cell Signaling 2021 aim is to bring together popular academicians, research scholars and researchers to share their experiences and this will results on all aspects of the Conference. It also provides a premier platform for researchers, participants, and educators to attend and discuss the most recent innovations.
Scope and Importance:
Cell Signaling 2021 aims to discover advances in Cell Signaling and Cancer Therapy and study about the early detection as well as treatment care based on Professional standards, and intense research to complete cure for whole Cancer. The Conference is to give a platform to academicians and practitioners from multiple disciplines to debate and deliberate on social change that is covered by innovation and technology.
Why to attend?
Cell Signaling 2021 is one of the world's leading conferences in the present scenario to bring together all the participants to exchange and bring discoveries of Cell Biology, Cancer Therapy, Cellular Signaling, Cellular Therapies, Cell Culture and Bioprocessing, etc.
Who can attend?
Cell Signaling 2021 brings together individuals who have an interest in different fields of Genetic Engineering like Immunologists, Biotechnologists, Health-care professionals, Cell and Cancer therapy Faculties & associations. It is a forum to discover issues of mutual concern as well as exchange knowledge, share evidence, thoughts, and make solutions.
Target Audience:
- Researchers and Students
- Biotechnologists
- Academicians
- Immunologists
- Practitioners
- Pharmaceutical Experts
Track 1: Cellular Signaling
Cells respond to a multitude of signals in the extracellular environment, often by activating intracellular signaling pathways that elicit changes in cell function or behavior. These signaling pathways may be activated in response to growth factors, cytokines, or other signaling molecules, leading to intracellular activation of kinase pathways. CST offers a comprehensive portfolio of the highest quality products to interrogate molecular signaling networks. Replacing a disease-causing gene with a healthy copy of the gene. Inactivating a disease-causing gene that is not functioning properly. Introducing a new or modified gene into the body to help treat a disease
- Map Kinase Signaling
- Ca, cAMP, Lipid Signaling
- AKT Signaling
- Receptor Tyrosine Kinase Signaling
- Growth factors and Cytokines
Track 2: Cell Science and Stem Cell Research
Stem Cell Research & Therapy is the major domain for translating analysis into stem cell therapies. An international peer-reviewed conference, it publishes high-quality open research access articles with a special stress on basic, translational and clinical research into stem cell therapeutics and regenerative therapies, including animal models and clinical trials. The conference also provides reviews, viewpoints, commentaries, reports and strategies. They are some specified stem cells given below.
- Adult stem cells
- Embryonic stem cells
- Induced pluripotent stem cells
- Cancer stem cells
- Stem cell differentiation, proliferation and migration
- Cell culture and manufacture
- Stem cell therapy/transplantation
- Ethical, legal and social aspects
Track 3: Cell Culture and Bioprocessing
Stem cells are the basic materials of body cells from that all different cells will be specialized and functions are generated. Below the proper condition with in the body or a laboratory, stem cells divide to create a lot of cells called daughter cells.
These daughter cells will either become new stem cells (self-renewal) or else become specialized cells with a more specific function, such as blood cells, brain cells, heart muscle cells or bone cells. No different cell with in the body has the natural ability to generate new type of cell.
- Increase understanding of how diseases occur
- Generate healthy cells to replace diseased cells (regenerative medicine)
- Test new drugs for safety and effectiveness
- Embryonic stem cells
- Adult stem cells
- Adult cells altered to have properties of embryonic stem cells
- Perinatal stem cells
Track 4: Stem Cell Therapies
Stem cells are constant cells found in cell living organisms that get separated through a cell division and then gets separate into a particular cell. The two properties of foundational microorganisms which are used to separate them in very body cell are self-restoration and proficiency. Because of their prospective job in different conducts, a foundational microorganism is subjected as inside and outside examination of Extensive Research Science.
- Biology of Human Embryonic Stem Cells.
- Genomics and Genetics in Somatic Cell Biology
- Cell signal in Somatic Cell Differentiation.
- In-vitro culturing of Stem Cells.
- Applications of Somatic Stem Cells.
Track 5: Stem Cell in Drug Development
Undefined cell treatment has been opened another way in the territory of medication disclosure and improvement. Biopharmaceutical organizations have been working in interpreting fundamental utilizations of undefined cell advances in the medication improvement forms in order to diminish the high weakening rate generally arrange sedate applicants, which has been developing at a quick place in the previous decade.
Approach of unformed microorganism advances has given new expectation to fabricate imaginative cell models. The always developing systems utilized for detachment of human/creature embryonic foundational microorganisms (ESCs), bone marrow-determined mesenchyme developed cells, umbilical line undifferentiated organisms, grown-up tissue-particular neural immature microorganisms and human instigated pluripotent foundational microorganisms (iPSC) have prompted the headway of varied high throughput and combinatorial screening advancements consequently supplementing the a part of undifferentiated organism models in sedate disclosure.
- Cancer Clinical Trails
- Clinical Research And Bioethics
- Drug Screening Tools
- Stem Cell Biology And Regenerative Medicine
- Drug Safety And Regulations
Track 6: Nanotechnology in Stem Cell
In recent years, stem cell nanotechnology has emerged as a replacement of exciting field. Experimental and Theoretical studies of interaction between nanostructures or nanomaterial’s and stem cells have created nice advances. The importance of nanotechnology, nanostructures, and nanomaterial’s to the elemental developments in stem cells-based therapies for injuries and degenerative diseases has been recognized. In general, the consequences of properties and structure of nanomaterials on the accretion and differentiation of stem cells became a replacement of integrative border in reconstruction medicine and material science
- Nanoparticles: Cell Tracking, And Endocytosis
- Nano vaccines
- Nanomaterial’s And Nano engineering
- Nanotechnology For Genetic Engineering
- Nanotechnology For Creating Stem Cell Niche
- Nanoparticle Toxicity To Stem Cells
Track 7: Cell Death and Viability
Understanding the mechanisms that cause cell death is a critical aspect of cell biology, as many diseases involve aberrant regulation of cell death mechanisms. CST offers a variety of assays and reagents designed to enable evaluations of cell viability and cell death. LQT Syndromes.
- Apoptosis
- DNA Damage/Senescence
- Autophagy
- REDOX/Energy Metabolism
Track 8: Epidermis Stem Cell & Cancer Epidemiology
The skin gradually re-establishes itself for the duration of grown-up life, and the hair follicle experiences a never ending cycle of development and decay. Microorganisms (Stem Cell’s) lives in the epidermis and hair follicle guarantee the support of grown-up skin equilibrium and hair recovery; however they likewise take part in the fix of the epidermis after wounds.
- Stem Cells With In Adult Skin Epithelium
- Signalling And Stem Cell Fate Specification In The Skin
- Bone Morphogenetic Protein Signalling
- Notch Signalling
Track 9: Cell Cycle/Proliferation
Cell proliferation is required for tissue growth, development, maintenance, and repair. Disruptions to the cell cycle that governs proliferation are a root cause of many diseases, most notably cancer. CST has a diverse catalog of antibodies and assays to study cell cycle progression and checkpoint control. Novel Stem Cell Therapy For Knees
- Cell Cycle
- DNA Damage/Senescence
- Nucleotide metabolism
Track 10: Cellular Therapies
Cell therapy (also called cellular transplantation, cell therapy, or cytotherapy) is a therapy in which possible cells are injected, implant or embed into a patient in order to effectuate a medicinal effect, for example, by transplanting T-cells capable of fighting cancer cells via cell-mediated immunity in the course of immunotherapy, or grafting stem cells to regenerate diseased tissues.
Cell therapy commenced in the nineteenth century when scientists experimented by injecting animal material in a try to prevent and treat illness. However, such try didn’t produced any positive benefit, the next research was found in the mid twentieth century that human cells could be used to help prevent the human body rejecting transplanted organs, leading in time to successful bone marrow transplantation has become common practice in treatment for patients that have compromised bone marrow after disease, infection, radiation or chemotherapy.
- Allogeneic Cell Therapy
- Autologous Cell Therapy
- Xenogeneic Cell Therapy
Track 11: Advanced Gene Therapeutics
The capability to make specific modifications to the human gene has been an objective in medical since; gene is the recognition of the basic unit for heredity. Therefore, gene therapy is defined as the capability of genetic improvement through the correction of modified genes or specific modifications that target therapeutic treatment. This therapy became possible through the advances of genetics and bioengineering that enabled manipulating vectors for delivery of extra chromosomal material to target cells. One of the major focuses on this technique is the optimization of delivery vehicles (vectors) that are mostly plasmas, unstructured or viruses. These viruses are more often investigated due to their excellence of infected cells and inserting their genetic material.
- Substitution of the adenosine deaminize deficiency
- Substitution of α 1-antitrypsin
- Improvement of immune function
- Tumour removal
- Chemo protection
- Enzymatic substitution
- Cytokine release
Track 12: Immunotherapy
Immunotherapy is considered as a type of cancer treatment that helps your immune system to fight against cancer. The immune system helps your body to fight with infections and other diseases. It is consists of organs and white blood cells and tissues of the lymph system.
Immunotherapy is a type of biological therapy. Organic therapy is a type of treatment that we use from the substances made from living organisms to treat cancer.
- Immune checkpoint inhibitors
- T-cell transfer therapy
- Monoclonal antibodies
- Immune system modulators
Track 13: Nano-Therapy
At the present scenario Cancer therapies are not basing on surgery, radiation, and chemotherapy. Because all these three methods cause a risk damage to normal tissues or incomplete destruction of the cancer. Nano- therapy means to target chemotherapies and also collectively to cancerous cells and neoplasms, guide in surgical resection of tumour and enhance the therapeutic competence of radiation-based and the other current based treatment methods. All these together can decrease the risk to the patient and an increased probability of survival.
- Delivering Chemotherapy
- Nano-enabled Immunotherapy
- Delivering or Augmenting Radiotherapy
- Delivering Gene Therapy
Track 14: Human Gene Therapy
Human gene therapy and its function for the treating the human genetic disorders, such as cystic fibrosis, cancer, and other diseases, are considered. Gene therapy is defined as a technique in which a functioning gene is stuck in into a human cell to correct a genetic error or else to introduce a new functioning to the cell. Many methods, including viral vectors and non-viral vectors, have been developed for both ex vivo and in vivo gene transfer into cells. There are several safety and ethical issues related to manipulating the human gene that need to be resolved. Current gene therapy efforts focus on gene insertion into stem cells only. The current human gene project provides the sequences of a vast number of human genes, leading to the identification, characterization, and understanding of genes that are responsible for many human diseases.
- Replacing a disease-causing gene with a healthy copy of the gene
- Inactivating a disease-causing gene that is not functioning properly
- Introducing a new or modified gene into the body to help treat a disease
- Plasmid DNA.
- Viral vectors
- Bacterial vectors
- Human gene editing technology
- Patient-derived cellular gene therapy products
Track 15: Molecular Epigenetics
Epigenetics is rising to eminence in biology as a mechanism by which environmental factors have intermediate-term effects on gene expression without changing the underlying genetic sequence. It can occur through the specific methylation of DNA bases and modification of histones. There are wide-feeding implications for the gene-environment contest and epigenetic mechanisms are causing a revaluation of many traditional concepts such as heritability. The reversible nature of epigenetics also provides conceivable treatment or prevention prospects for diseases previously thought hard-coded into the gene. Therefore, we consider how growing knowledge of epigenetics is altering our understanding of biology and medicine, and its implications for future research.
- Covalent modifications
- RNA transcripts
- MicroRNAs
- mRNA
- sRNAs
- Prions
- Structural inheritance
- Nucleosome positioning
- Genomic architecture
Track 16: Bioengineering Therapeutics
Therapeutics Engineering assembles understanding of bodily responses to imputable materials and drug delivery devices. These focus on the biomaterial selection and fusion and also in depth study of drug design, manufacturing, and delivery. We will be getting trained in Nano-materials, material properties, transport phenomena, biochemical engineering, and metabolic engineering. Application areas include analyse therapeutics, biomimetic, and drug delivery systems.
- Advancing technologies to detect and differentiate disease states and treatment responses (i.e., biomarkers) rapidly and precisely
- Developing low-cost sensors that detect subtle, early changes in health status, allowing for more rapid, effective interventions
- Synthesizing injectable microstructure biomaterials to reduce functionally debilitating scarring
- Creating methods and devices to deliver drugs across biological barriers, and to precisely target therapies to specific tissues and cells
- Building and miniaturizing fully implantable, bio artificial devices to carry out the natural functions of failed organs
- Building a solution for kidney failure
- Drug delivery for a leading cause of blindness
- Speeding genetic analysis of individual cells for disease biomarkers
- Delivering targeted, personalized cancer therapy to metastatic tumours
- Developing metabolic imaging technologies to detect cancer biomarkers
- Using microstructures to reduce debilitating scars after heart attacks
Track 17: Clinical Trials and Research in Stem Cell in Cancer Therapy
Almost every cell and gene therapy the clinical trial is dissimilar in some way. Working with living organisms presents new and dissimilar challenges to the traditional clinical trial model. With over 400 decades CGT professionals globally, ICON has developed tools and best practices to transform CGT trial design and implementation. From site selection to study start up through implementation, ICON supply project management, clinical services, product-specific logistics solutions, data flow, regulatory strategy and central laboratory services.
Track 18: Regulatory and Ethical Issues of Therapies.
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration's (FDA's) new Paediatric Rule makes it more likely that children will receive improved treatment, because physicians will have more complete information on how drugs affect children and the suitable doses for each age group (FDA, 1998e). The rule also allows FDA to require industry to test already marketed products in studies with paediatric populations in certain fascinating circumstances, such as when a drug is commonly prescribed for use in children but when the absence of adequate testing and labelling could be significant risks. The aim of this session is to examine many interrelated legal and regulatory issues, as well as the interrelated social and ethical concerns, in the evaluation of the effects of drugs and biologics on paediatric populations.
- Anchoring Studies to "Minimal Risk"
- Current Regulations Guiding Clinical Research
- Placebo-Controlled Trials
- Consent, Assent, and Determination of Risk
Track 19: Cell Biology:
Cell biology is the study of cell structure and function, and it spins around the concept that the cell is the basic unit of life. Centering on the cell permits a detailed understanding of the tissues and organisms that cells compose. A few organisms have only one cell, whereas others are organized into agreeable groups with huge numbers of cells. On the entire, cell biology centers on the structure and work of a cell, from the foremost common properties shared by all cells, to the special, profoundly complex functions particular to specialized cells.
Track 20: Regenerative Medicine:
Regenerative Medicine, the application of treatments developed to replace tissues damaged by injury or malady. These medicines may include the utilize of biochemical procedures to initiate tissue recovery specifically at the site of damage or the utilize of transplantation methods utilizing separated cells or stem cells, either alone or as a portion of a bio-artificial tissue.
The cell signaling market is expected to grow from USD 2.53 billion in 2017 to USD 3.51 billion by 2022, at a CAGR of 6.8%. This report aims to estimate the market size and potential for growth in the cell signaling market across different segments such as type, product, technology, pathway, applications, and regions. This study also provides detailed information regarding factors influencing the growth of the market such as drivers, restraints, challenges and opportunities.
Market Dynamics
Drivers
- Rising Incidence of Chronic Diseases
- Availability of Funding for Cell-Based Research
- Technological Advancements in Cell-Based Research Instruments
- Growth of End-Use Industries
Restraints
- High Cost of Cell Signaling Systems
- Ethical Issues Related to Embryonic Stem Cell Signaling Research
Opportunities
- Emerging Markets
- Emergence of Microfluidics in Cell Biology Research
Challenges
- Complexities Related to Antibody and Reagent Development
Availability of funding cell based research is key driver for the global cell signalling market
Governments of various countries are promoting and supporting cell-based research activities such as cell signalling, single-cell analysis, and stem cell research. A large portion of the funding from governments is provided to academic research societies to promote cell-based research, which helps in the evaluation of diagnostic and therapeutic applications of various types of cells in the management of chronic and infectious diseases. By driving research into the application and end-user industries for cell analysis, the availability of support plays a significant role in aiding market growth.
Objectives Of The Study
- To define, describe, and forecast the cell signaling market on the basis of signaling type, product, technology, pathway, application, and region
- To provide detailed information regarding the major factors influencing growth of the market (drivers, restraints, and opportunities)
- To strategically analyze micromarkets1 with respect to individual growth trends, future prospects, and contributions to the overall market
- To analyze the opportunities in the market for stakeholders and provide details of a competitive landscape for market leaders
- To forecast revenue of the market segments with respect to four main regional segments, namely, North America, Europe, Asia, and the Rest of the World (RoW)2
- To profile key players and comprehensively analyze their market shares and core competencies3 in terms of market development and growth strategies
- To track and analyze competitive developments such as agreements, collaborations, and partnerships; acquisitions; and product launches in the cell signaling market
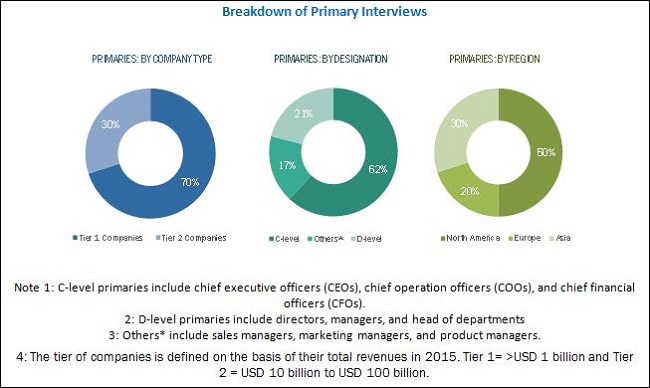
The research methodology used to estimate and forecast the cell signaling market begins with capturing data from secondary sources such as WHO, NCBI, UN DESA, GLOBOCAN, CRG, and others. The bottom-up procedure was employed to arrive at the overall market size of the cell signaling market from the revenue of the key players. After arriving at the overall market size, the entire market was split into several segments and subsegments which are then verified through primary research by conducting extensive interviews with CEOs, VPs, directors, executives, and others.
The cell signaling ecosystem comprises reagent and antibody manufacturers such as Merck KGaA (Germany), Becton, Dickinson and Company (U.S.), Beckman Coulter, Inc. (U.S.) (a subsidiary of Danaher Corporation), Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc. (U.S.), Bio-Rad Laboratories, Inc. (U.S.), QIAGEN N.V. (Netherlands), PerkinElmer Inc. (U.S.), Promega Corporation (U.S.), Bio-Techne Corporation (U.S.), Cell Signaling Technology, Inc. (U.S.), Abcam plc (U.K.), Miltenyi Biotec (Germany), Cell Biolabs, Inc. (U.S.), Full Moon BioSystems, Inc. (U.S.), Cisbio Bioassays (France), BioVision, Inc. (U.S.), Rockland Immunochemicals Inc. (U.S.), Tonbo Biosciences (U.S.), StressMarq Biosciences Inc. (U.S.), BPS Bioscience, Inc. (U.S.), Abeomics, Inc. (U.S.), RayBiotech, Inc. (U.S.), MEDICAL & BIOLOGICAL LABORATORIES CO.,LTD. (Japan), Sino Biological, Inc. (U.S.), and Santa Cruz Biotechnology, Inc. (U.S.).
Major Market Developments
- In 2016, Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc. (U.S.) acquired FEI Company (U.S.) to strengthen its high-performance electron Microscopy business.
- In 2017, Becton, Dickinson and Company (U.S.) launched BD Resolve Single-Cell Gene Expression platform. This has strengthen the position of company in cell signalling market.
- In 2016, Cell Signaling Technology Inc. (U.S.) launched CellSimple Cell Analyzer. This helped company to strengthen the presence in cell signalling market.
Key Target Audience:
- Cell signaling associations
- Research & consulting firms
- Distributors of cell signaling research products
- Contract manufacturers of cell signaling consumables and instruments
- Research institutes and clinical research organizations (CROs)
- Venture capitalists
- Government associations
Critical questions the report answers
- How the market developments of key players impact the overall industry?
- What are the restraining factors for this market?
Available Customization Options:
With the given market data, MarketsandMarkets offers customizations as per the company’s specific needs. The following customization options are available for the report:
- Company Information: Detailed company profiles of five or more market players
- Opportunities Assessment: A detailed report underlining the various growth opportunities presented in the market
The cell signaling market is projected to reach USD 3.51 billion by 2022 from USD 2.53 billion in 2017, at a CAGR of 6.8%. The term “cell signaling” is used to define the complex interactive system of signals that regulates and mediate various cellular responses in the human body.
Cell signaling is used to study signaling pathways of cells in drug discovery and therapeutic development, to distinguish drug resistance patterns in cancerous cells. It also identifies the major signaling pathways impacted by specific drug treatments. Cell signaling pathways—also called signal transduction pathways—act as connecting links between environmental stimuli and the corresponding cellular response. These signaling pathways mainly consist of proteins that can interact, move to specific locations, or be modified.
Growth in the Medical Supplies market is primarily driven by rising incidence of chronic diseases, and availability of funding for cell-based research activities. Other factors that are also positively affecting the growth of this market are technological advancements in cell-based research instruments and growth in life science and biopharmaceutical industries. However, ethical issues related to embryonic stem cell signaling research and the high cost of cell signaling systems are expected to hinder the growth of this market.
Based on the type, the cell signaling market is segmented into paracrine, autocrine, endocrine, juxtacrine, and other signaling types (neuronal and intracrine). The endocrine signaling segment is estimated to account the largest share of cell signaling market in 2017.
By product, the cell signaling market is segmented into consumables (reagents, assay kits, antibodies, and other consumables) and instruments. In 2017, the consumables segment is estimated to account the largest share of the cell signaling market.
Based on technology, the cell signaling market is segmented into microscopy, western blotting, immunohistochemistry (IHC), flow cytometry, enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA), mass spectrometry, and other technologies (immunofluorescence and immunoprecipitation). The microscopy segment is estimated to account the largest share of cell signaling market in 2017.
Based on application, the cell signaling market is segmented into research applications (stem cell, immunology, cancer, and other research applications), and medical applications. The research applications segment is estimated to account the largest share of cell signaling market in 2017.
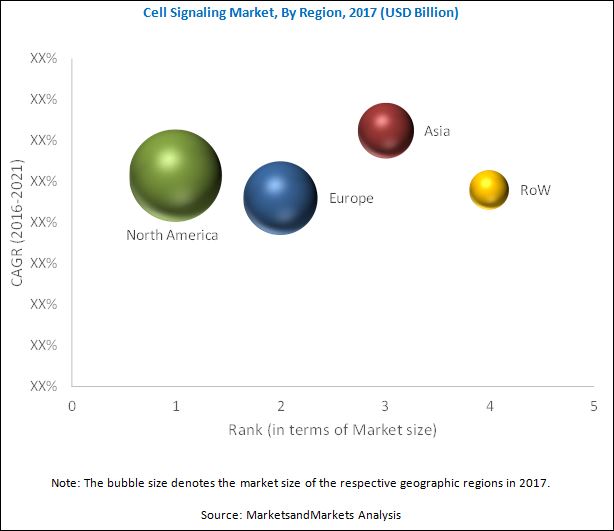
In 2017, the medical supplies market is dominated by North America, followed by Europe. North America is expected to continue to dominate the market by 2022. Asia is projected to witness the highest CAGR, centered at China, Japan, and India, during the forecast period.
Conference Highlights
- Cellular Signaling
- Cell Science and Stem Cell Research
- Cell Culture and Bioprocessing
- Stem Cell Therapies
- Stem Cell in Drug Development
- Nanotechnology in Stem Cell
- Cell Death and Viability
- Epidermis Stem Cell & Cancer Epidemiology
- Cell Cycle/Proliferation
- Cellular Therapies
- Advanced Gene Therapeutics
- Immunotherapy
- Nano-Therapy
- Human Gene Therapy
- Molecular Epigenetics
- Bioengineering Therapeutics
- Regulatory and Ethical Issues of Therapies.
- Clinical Trials and Research in Stem Cell in Cancer Therapy
- Cell Biology
- Regenerative Medicine
To share your views and research, please click here to register for the Conference.
To Collaborate Scientific Professionals around the World
| Conference Date | November 24-25, 2021 | ||
| Sponsors & Exhibitors |
|
||
| Speaker Opportunity Closed | |||
| Poster Opportunity Closed | Click Here to View | ||
Useful Links
Special Issues
All accepted abstracts will be published in respective Our International Journals.
Abstracts will be provided with Digital Object Identifier by
